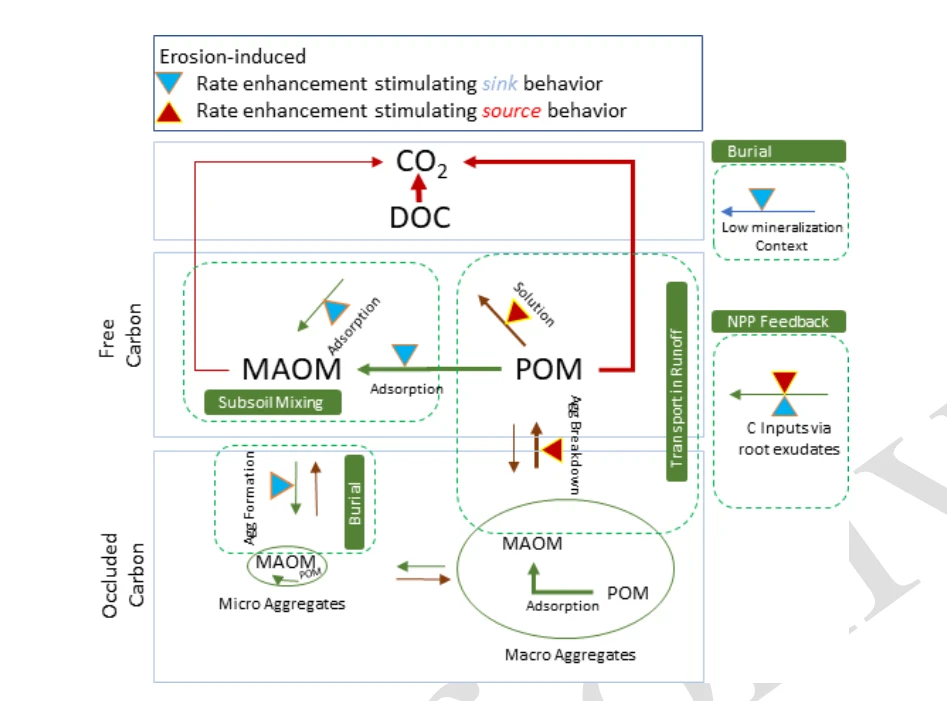
Schematic representation of the effect of water erosion and deposition on soil OC stabilization and loss processes
Transport in runoff: detachment and transport can shift OC from a protected state in aggregates to an available state where it mineralizes more rapidly.
Burial: the deposition of eroded OC moves OC into a low-mineralization context and can also enhance protection via aggregation.
Subsoil mixing: at sites of erosion new OC formation from new vegetation inputs into exposed subsoil by erosion may replace some of the eroded.
OC. Net primary production (NPP) feedback: erosion and deposition may affect the nutrient and soil depth status (and hence soil fertility) as well as the environmental factors that control OC input versus output.
Related EGU articles
- New study settles long-standing debate: does agricultural erosion create a carbon sink or source (16 February 2023)
Download
- Original image (142.5 KB, 947.0x701.0 px)